Why do animals need a transport system? Think of the things all cells need….where do they get them from?
Oxygen……from the air via the lungs
Nutrients and water…….from eating and drinking via the gut
Cells also need to get rid of wastes such as carbon dioxide
How do these things actually get to the cells?
BLOOD!
The blood picks these things up and carries them around the body delivering them to the cells (and takes wastes away from cells to be removed from the body)
The RED BLOOD CELLS (RBCs) pick up OXYGEN in the lungs and carry it to the body cells.
RBCs are structurally adapted to do this efficiently – they are BICONCAVE DISCS which increases their surface area to increase their ability to pick up oxygen. They are also jam packed full of the red pigment HAEMOGLOBIN which binds to oxygen and forms OXYHAEMOGLOBIN. This breaks down in the low oxygen conditions of the body tissues to release the oxygen to the body cells.

Blood travels in BLOOD VESSELS of which there are 3 types:
- ARTERIES carry blood AWAY from the heart (I remember this as AA…Away in Arteries) Arteries have to cope with blood under high pressure and so they have thick muscular walls which allow them to expand with each pressure wave of blood caused by each heart beat (and felt as a PULSE when the artery is close to the surface). The blood in arteries is oxygenated and arteries have no valves.
- CAPILLARIES connect arteries and veins. The capillaries are microscopic and run close to every body cell. The exchange of materials occurs in the capillaries – oxygen and food to the cells and carbon dioxide from the cells. To make them efficient at this function, capillaries have a one cell thick wall and a large surface area.
- VEINS carry blood back TOWARDS the heart (TV Towards the heart in Veins). The blood is deoxygenated now and at low pressure and so the veins have thinner walls. To prevent the blood flowing the wrong direction veins have VALVES.
The HEART is a muscular pump that keeps the blood going around the body.
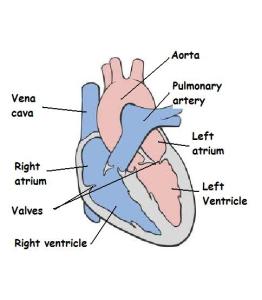
It is made up of 4 chambers – 2 upper ‘receiving chambers’ called ATRIA (That’s plural – the singular is ATRIUM) and 2 lower ‘pumping chambers’ called VENTRICLES. The chambers are separated by VALVES which stop blood going the wrong way.
The RIGHT hand side of the heart contains DEOXYGENATED blood that has returned to the heart from the body in the VENA CAVA. It travels through the RIGHT ATRIUM and RIGHT VENTRICLE and the heads to the lungs in the PULMONARY ARTERY. After being OXYGENATED in the lungs the blood returns to the heart in the PULMONARY VEIN and travels through the LEFT ATRIUM and VENTRICLE before heading off to the body in the AORTA.
Top tip – if you have a diagram of the heart to label – remember that the heart is FACING YOU…this means the left of the heart is on the right of the page.
The heart needs its own blood supply to provide the heart muscle with oxygen and food. These blood vessels are called the CORONARY ARTERIES. If one of these gets blocked it causes a heart attack. (Posh name is Myocardial infarction)

Now try an extended response question:
Blood travels in 3 types of blood vessels. Compare the structure of two of these vessels. (3 marks)
OR
Explain how the structure of a red blood cell is adapted to suit its function. (3 marks)